Better Together? In Industry 5.0 Humans Team Up with Robots

In the 1st Industrial Revolution, steam and water power were used to mechanize production. The 2nd Industrial Revolution came about as electricity was used for mass production with assembly lines.
 When robots were first introduced into manufacturing in the 1960s, the industry called it the 3rd Industrial Revolution or Industry 3.0. Besides robots, programmable logic controllers (PLC) and advanced manufacturing systems (AMS) were all the rage. Robots were primarily used for welding automobiles together, while PLCs and AMS were used to control the factory floor.
When robots were first introduced into manufacturing in the 1960s, the industry called it the 3rd Industrial Revolution or Industry 3.0. Besides robots, programmable logic controllers (PLC) and advanced manufacturing systems (AMS) were all the rage. Robots were primarily used for welding automobiles together, while PLCs and AMS were used to control the factory floor.
As technologies matured, robots were used in other areas such as logistics, medical or food industries. Industrial robots did all the dirty, menial, and repetitive tasks that humans didn’t like. Industrial robots are typically kept behind some safety barrier to protect humans as the machinery performs heavy duty manufacturing tasks.
When sensors started being embedded in equipment of all types, the move to intelligent automation was born and named Industry 4.0. Connected automation technologies form the backbone of Industry 4.0. These technologies are making important differences in the manufacture of many types of products, enabling mass customization of low cost, high quality, unique products.
With Industry 4.0, disparate systems connect to share information and optimize manufacturing. Industry 4.0 technologies can shorten cycle times, improve product quality, and increase efficiencies. Industry 4.0 shifts manufacturing from isolated, silos of business processes, systems and resources to fully integrated data and product flows across the enterprise, its customers, and its suppliers.

The Fourth Industrial Revolution takes what was started in the third revolution with the adoption of computers and automation and enhances it with smart and autonomous systems fueled by data and machine learning. As smart machines get smarter with access to more data, manufacturing processes will become more efficient and productive and less wasteful.
While we are still in the Fourth Industrial Revolution today, we are moving towards the fifth revolution.
Industry 5.0 – People want mass personalization, which can be achieved when human touch returns to manufacturing. The 5th Industrial Revolution brings smaller, more personalized batches of products to market. Consumers want to stand out as unique and personalized products enable them to express themselves as individuals.
Quality magazine says, “This desire for mass personalization forms the psychological and cultural driver behind Industry 5.0, which involves using technology to return human value-add to manufacturing.”
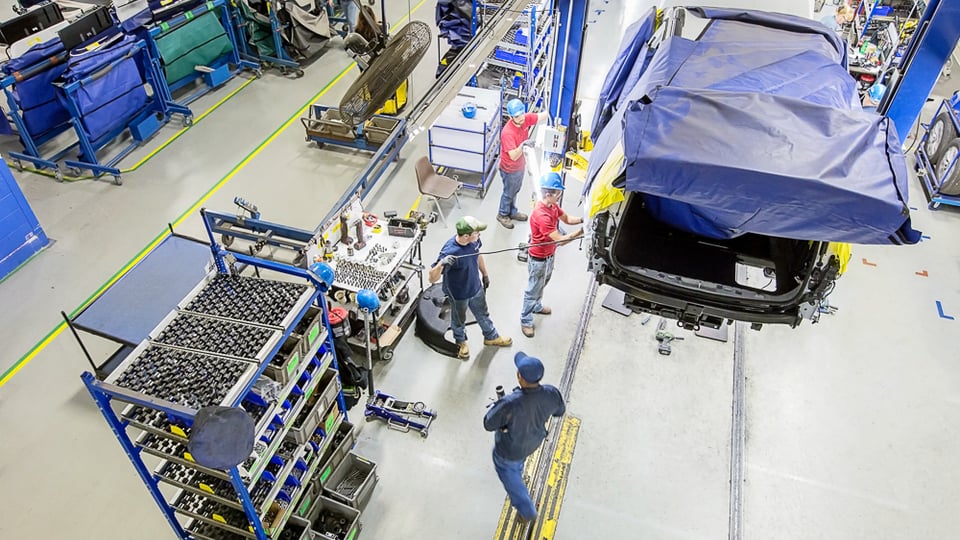
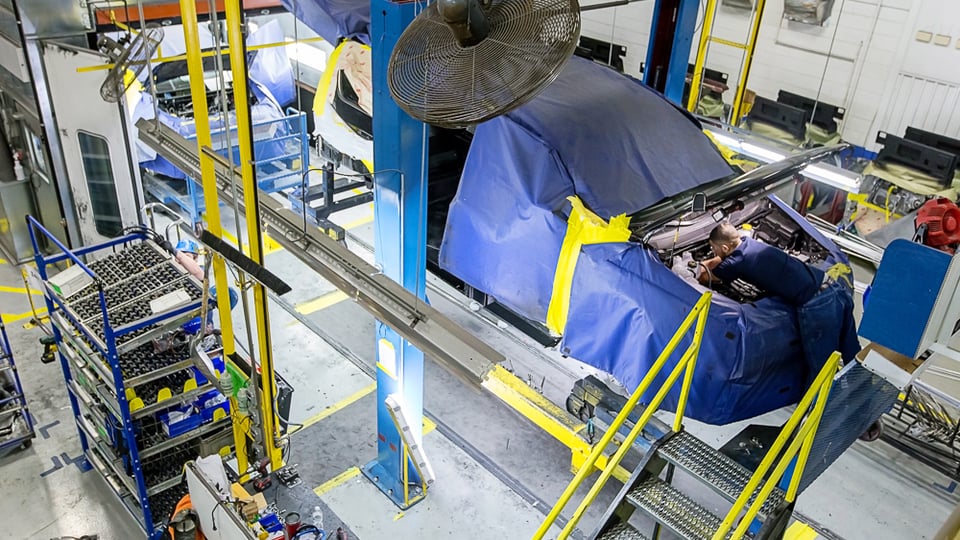
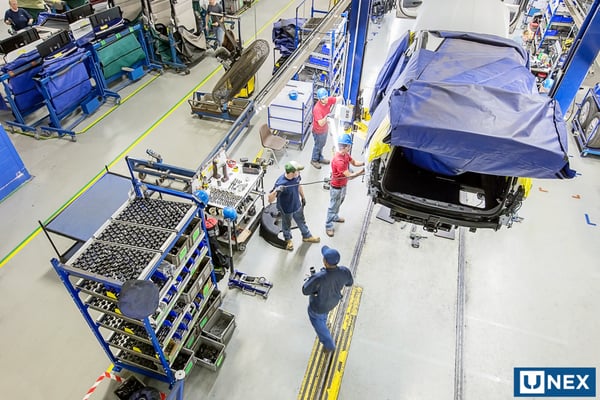
Industry 5.0 is the age of collaborative robots (cobots), which are robots that work in conjunction with people, to facilitate the “human touch” in the manufacturing process.
Personalized products require human involvement. People want products that have been designed by humans and made by craftspeople – luxurious products at a price that people can afford. Collaborative robots facilitate this process.
Collaborative robots are exactly the tools companies need to produce the personalized products consumers demand today. Collaborative robots bring the human touch to automated processes, adding speed and precision. And these robots are becoming smarter, equipped with more sensors, so they can be more reactive, helping manufacturers increase the speed of innovation and deliver on customer preferences.
UNEX solutions like Span-Track and Flow Cell help businesses be more efficient and more profitable but still rely on the human touch for each picking and selection, an area where robots aren't yet cost-effective.